金桔
金币
威望
贡献
回帖0
精华
在线时间 小时
|
登陆有奖并可浏览互动!
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册


×

犬和猫的肾脏疾病很常见;估计患病率在7%到20%之间。国际肾脏协会(IRIS)已经制定了肾脏疾病临床分期和分级指南,其中包括急性肾损伤(AKI)和慢性肾病(CKD)的标准。这些指南已帮助兽医识别可能通过治疗干预缓解的肾损伤或疾病病例。然而,尽管肾脏疾病具有临床意义,但早期发现肾损伤仍然具有挑战性。
肾功能最准确的评估被认为是肾小球滤过率(GFR)的测量。然而,这种方法劳动强度大且耗时,使其在日常临床实践中成为不切实际的测试。使用血清肌酐和血尿素氮(BUN)间接评估肾功能很容易进行,并且这些测试广泛可用。然而,这两种分析物都有公认的局限性,导致对肾脏疾病的检测缺乏敏感性和特异性。直到大约75%的功能性肾单位丧失前这些值通常都不会增加。
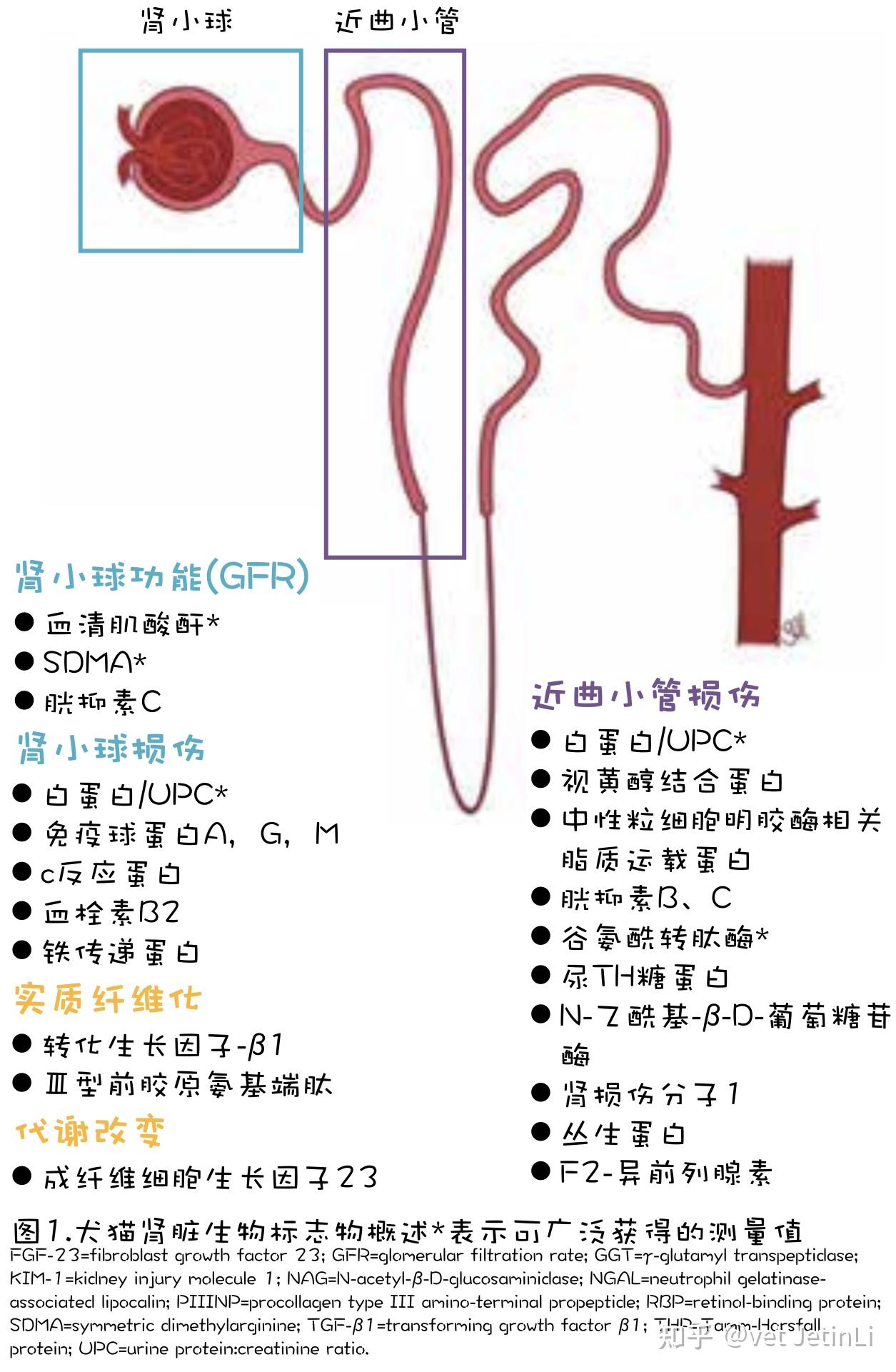
识别肾脏损伤和疾病的新生物标志物很有吸引力,并将为诊断和监测受影响的犬和猫提供额外的工具。检测肾脏疾病的理想生物标志物应具有特异性(即不受并发症的影响),与GFR密切相关,并且在检测疾病方面比血清肌酐更敏感。此外,理想的生物标志物可用于确定损伤的严重程度和位置,以及监测疾病进展或治疗反应,并且可从参考实验室或临床试验中随时获得检测结果。一些有希望的候选标志物被发现在临床和研究环境中有助于评估肾脏疾病(图1)。这篇综述描述了目前关于犬和猫广泛使用的肾脏生物标志物的证据及其在临床实践中的潜在用途。
血液中的肾脏生物标志物
两种最常用的血清生物标志物是肌酐和对称二甲基精氨酸(SDMA),可广泛用于检测。
肌酐
最广泛使用的肾功能(GFR)间接标志是血清肌酐。虽然这篇综述主要关注新的肾脏生物标志物,但我们需要考虑血清肌酐临床应用的几个基本因素,以帮助临床医生解释结果。
人们普遍认为,血清肌酐与GFR成反比和指数相关,高于参考区间的肌酐与约50%至60%的肾功能丧失相关。血清肌酐的敏感性差部分源于个体之间的高变异性,导致基于群体的参考区间较宽。在个体犬或猫中观察到数周至数月的低变异性意味着血清肌酐的小幅增加,即使在参考范围内间隔,可能反映肾功能显著下降。因此,血清肌酐检测肾脏疾病的敏感性可能可以通过评估个体患者的连续测量来提高。
仪器和实验室之间血清肌酐测量值的巨大差异会导致结果明显不同,这可能会影响个体患者趋势结果的临床解释。研究表明,在不同仪器或不同实验室测量的单个样品的血清肌酐结果范围为0.9至2.3mg/dL。因此,为了尽量减少这种显著的分析变异,对特定患者的血清肌酐进行连续测定应在同一台分析仪或同一实验室始终如一地进行。
血清肌酐测量的另一个重要的固有限制是它对肌肉量的依赖性。许多肾病患者是老年或恶病质;肌肉量下降会导致血清肌酐下降,从而导致肾功能被高估。也就是说,在患有肾脏疾病的动物中,导致肌酐增加的GFR减少可能被肌肉消耗抵消。因此,对连续肌酸酐测量的解释必须考虑肌肉量的变化,肌酐可能是并发肌肉萎缩患者肾功能下降的不可靠指标。
SDMA
SMDA是一种甲基化氨基酸(精氨酸),主要由肾脏排泄,似乎不会被肾小管重吸收再利用。开发并验证了高通量免疫测定法,使SDMA成为IDEXXLaboratories,Inc.(http://idexx.com)提供的化学检测板上的标准分析物;犬和猫的衍生参考值≤14μg/dL。SDMA是犬和猫中GFR的内源性替代标志物;它与GFR的指数关系类似于血清肌酐的指数关系,并已纳入IRIS分期系统。纵向临床研究表明,SDMA可以潜在地用于检测一些患者肾功能的早期下降,并作为CKD的早期标志物。然而,它对监测CKD进展的有用性还没有被很好地确定。SDMA的个体内和分析变异高于血清肌酐,这可能使其更难跟踪肾功能随时间的真实变化。在犬中,需要大约6μg/dL的测量值之间的临界差异来指示连续SDMA浓度的临床显著变化。
与血清肌酐不同,SDMA似乎不受肌肉质量的影响,并已被证明与成年犬和老年猫的瘦体型无关。然而,最近的研究提供了初步证据,表明SDMA的浓度可能会受到糖尿病、肿瘤(淋巴瘤)和肾结石等疾病的影响。此外,有报道称,SDMA升高的动物肾功能正常。这些报告强调了进一步研究探索非肾脏疾病对SDMA浓度影响的必要性。
尿液中的肾脏生物标志物
使用尿液生物标志物进行AKI的早期检测在兽医专业中是一个有价值的关注领域。这些生物标志物可以帮助从业者在肾损伤的早期阶段确定干预的机会,此时他们可能有机会防止额外的损害,特别是对于正在接受肾毒性药物治疗或暴露于AKI的其他风险因素(例如,败血症、毒素暴露、近期手术)的患者。尿液生物标志物包括肾性蛋白尿、中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白(NGAL)和γ-谷氨酰转肽酶(GGT)。
肾性蛋白尿
持续性肾性蛋白尿与犬和猫的肾脏疾病进展和死亡风险增加有关。在小动物临床中,持续性肾性蛋白尿常常被忽视为肾脏疾病的早期标志物。通常直到发生氮质血症才被发现,从而导致错过及时治疗干预的机会。减轻蛋白尿的治疗与延缓肾脏疾病进展和改善犬的生存结果有关。
蛋白尿是指尿液中的任何类型的蛋白质。其主要机制有两种:选择性肾小球滤过功能丧失(导致滤液中血浆蛋白增加)或滤过蛋白的肾小管吸收受损。检测蛋白尿的第一线筛选试验是尿液试纸比色试验。如果蛋白尿持续存在,应量化尿蛋白与肌酐比值(UPC);猫的值>0.4,犬的值>0.5被认为是尿蛋白。历史上,UPC>2被认为与肾小球损伤更相关;然而,最近的证据表明,蛋白尿的大小并不总是用来确定肾小球或肾小管损伤导致的肾性蛋白尿。
近年来,在确定猫犬肾损伤蛋白尿模式方面的最新进展包括尿电泳(SDS-PAGE[十二烷基硫酸钠聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳])。 原发性肾小管损伤产生低分子量的蛋白质,原发性肾小球损伤产生中分子量到高分子量的蛋白质。 然而,蛋白尿犬的主要模式是混合的,这表明对肾小球和肾小管的损伤是常见的 需要进一步的研究来确定尿电泳是否可以预测疾病结果,记录治疗干预的有效性,或帮助临床医生确定哪些患者将受益于更具侵入性的全面肾活检。
NGAL
NGAL是一种新兴的临床检测肾小球和肾小管间质损伤的尿液生物标志物。在健康动物中,这种低分子量蛋白质自由通过肾小球膜,并几乎完全被肾脏近端小管重吸收。越来越多的证据表明NGAL可以作为AKI的生物标志物。最近,已经探索了这种生物标志物在接受肾毒性药物(例如氨基糖苷类)的犬和猫中用于识别早期肾损伤(与血清肌酐相比)的有效性。一项研究表明,在给予庆大霉素的犬中,NGAL在肌酐前几天显著增加。这一发现可能使我们能够更密切地监测患者的药物性肾损伤,从而对当前的治疗做出明智的决定。使用NGAL作为肾损伤的生物标志物的主要限制是其增加可由肾外原因(即下泌尿道疾病)引起。由于脓尿样本中的尿NGAL浓度会显著增加,因此临床医师应谨慎解读患有并发下泌尿道疾病的患者的尿NGAL结果。
GGT
GGT是近端肾小管上皮细胞中的刷状缘酶,可随着肾小管损伤的发作释放到尿液中。由于其大分子大小,血浆GGT不能自由地通过肾小球膜过滤;因此,只要肾小球屏障完好无损,尿液中GGT浓度的增加就可以可靠地反映肾小管损伤。这种管状酶可以通过使用用于测量犬和猫血清或血浆中GGT的相同分析仪在尿液中进行常规测量。健康动物的尿GGT通常含量较低。正在确定尿液GGT的参考范围;多项研究引用了健康成年犬的不同值。尽管从业者可能不会常规测量尿液GGT,但对于肾小管损伤风险增加的患者(例如接受肾毒性药物的患者)而言,这样做可能是一种谨慎的做法。连续GGT测量可以识别早期AKI,并为监测AKI治疗反应提供潜在机制。
未来展望
当前标志物
关于SDMA,需要进一步研究以确定该标志物是否对监测和预测疾病结果更敏感,并探索其他非肾脏因素对SDMA浓度的影响。此外,如果SDMA确实允许早期诊断CKD或AKI,则需要进一步研究以确定如何最好地管理这些患者。对于UPC,虽然测量该比率是评估肾蛋白尿的必要诊断步骤,但其在确定肾损伤的来源和严重程度方面的低特异性导致需要更特异性的肾小球和肾小管损伤尿液标志物。
未来标志物
兽医研究中感兴趣的几个肾脏生物标志物有望成为未来临床应用的工具,用于识别和监测肾脏损伤和疾病(图1)。兽医研究视野中的几个标志物已显示为肾小球损伤的特定指标,包括免疫球蛋白(A、G和M)、C反应蛋白、血栓素B2和转铁蛋白。同样,许多肾小管损伤标志物也在研究中,包括RBP(视黄醇结合蛋白)、胱抑素B和C、THP(TammHorsfall蛋白)、NAG(N-乙酰-β-D-糖胺酶)、KIM-1(肾损伤分子1)、clusterin和F2异前列腺素。此外,还发现了肾实质纤维化(TGF-β1[转化生长因子β1]和PIIINP[Ⅲ型前胶原氨基端肽])和肾代谢改变(FGF-23[成纤维细胞生长因子23])的一些标志物。这些生物标志物的测定可能会更广泛地用于临床诊断和早期肾损伤的定位。在测量这些生物标志物之前,还需要进行更多的研究,以便有信心地为此目的进行开发,但临床医生应在未来几年牢记这些研究。
结论
在评估患有肾病的犬和猫的各种新生物标志物方面取得了重大进展。然而,用于肾功能和损伤的商业化测试数量有限,需要进一步研究。这篇文章强调了几个新的生物标志物,它们可能有助于早期检测、监测和评估患有肾脏疾病的犬猫的预后。单个生物标志物不太可能提供单个动物的肾功能或损伤的完整全面的情况。更有可能的是,我们需要一组标志物来给我们一个全面的肾脏健康评估。

参考文献
1. Lund EM, Armstrong PJ, Kirk CA, et al. Health status and population characteristics of dogs and cats examined at private veterinary practices in the United States. JAVMA. 1999;214(9):1336-1341.
2. Kerl ME, Cook CR. Glomerular filtration rate and renal scintigraphy. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2005;20(1):31-38.
3. Haller M, Müller W, Binder H, Arnold P. Single-injection inulin clearance–a simple method for measuring glomerular filtration rate in dogs. Res Vet Sci. 1998;64(2):151–156.
4. Hokamp JA, Nabity MB. Renal biomarkers in domestic species. Vet Clin Pathol. 2016;45(1):28-56.
5. Braun JP, Lefebvre HP, Watson AD. Creatinine in the dog: a review. Vet Clin Pathol. 2003;32(4):162-179.
6. Bovée KC, Kronfeld DS, Ramberg C, Goldschmidt M. Long-term measurement of renal function in partially nephrectomized dogs fed 56, 27, or 19% protein. Invest Urol. 1979;16(5):378–384.
7. Finch N. Measurement of glomerular filtration rate in cats: methods and advantages over routine markers of renal function. J Feline Med Surg. 2014;16(9):736-748.
8. Baral RM, Dhand NK, Freeman KP, et al. Biological variation and reference change values of feline plasma biochemistry analytes. J Feline Med Surg. 2014;16(4):317-325.
9. Pagitz M, Frommlet F, Schwendenwein I. Evaluation of biological variance of cystatin C in comparison with other endogenous markers of glomerular filtration rate in healthy dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2007;21(5):936-942.
10. Ruaux CG, Carney PC, Suchodolski JS, et al. Estimates of biological variation in routinely measured biochemical analytes in clinically healthy dogs. Vet Clin Pathol. 2012;41(4):541-547.
11. Braun JP, Cabé E, Geffré A, et al. Comparison of plasma creatinine values measured by different veterinary practices. Vet Rec. 2008;162(7):215-216.
12. Ulleberg T, Robben J, Nordahl KM, et al. Plasma creatinine in dogs: intra- and inter-laboratory variation in 10 European veterinary laboratories. Acta Vet Scand. 2011;53(1):25.
13. Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, et al. Comparison of serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine as kidney function biomarkers in healthy geriatric cats fed reduced protein foods enriched with fish oil, L-carnitine, and medium-chain triglycerides.Vet J. 2014;202(3):588–596.
14. Kakimoto Y, Akazawa S. Isolation and identification of N-G,N-G- and N-G,N’-G-dimethyl-arginine, N-epsilon-mono-, di-, and trimethyllysine, and glucosylgalactosyl- and galactosyl-delta-hydroxylysine from human urine. J Biol Chem. 1970;245(21):5751-5758.
15. Relford R, Robertson J, Clements C. Symmetric dimethylarginine: improving the diagnosis and staging of chronic kidney disease in small animals. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2016;46(6):941-960.
16. Nabity MB, Lees GE, Boggess MM, et al. Symmetric dimethylarginine assay validation, stability, and evaluation as a marker for the early detection of chronic kidney disease in dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2015;29(4):1036-1044.
17. Braff J, Obare E, Yerramilli M, et al. Relationship between serum symmetric dimethylarginine concentration and glomerular filtration rate in cats. J Vet Intern Med. 2014;28(6):1699-1701.
18. Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, et al. Comparison of serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine as kidney function biomarkers in cats with chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2014;28(6):1676-1683.
19. Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, et al. Serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine in dogs with naturally occurring chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2016;30(3):794-802.
20. Pelander L, Häggström J, Larsson A, et al. Comparison of the diagnostic value of symmetric dimethylarginine, cystatin C, and creatinine for detection of decreased glomerular filtration rate in dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2019;33(2):630-639.
21. Kopke MA, Burchell RK, Ruaux CG, et al. Variability of symmetric dimethylarginine in apparently healthy dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2018;32(2):736-742.
22. Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, et al. Relationship between lean body mass and serum renal biomarkers in healthy dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2015;29(3):808-814.
23. Langhorn R, Kieler IN, Koch J, et al. Symmetric dimethylarginine in cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and diabetes mellitus. J Vet Intern Med. 2018;32(1):57-63.
24. Hall JA, Yerramilli M, Obare E, et al. Serum concentrations of symmetric dimethylarginine and creatinine in cats with kidney stones. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174854.
25. King JN, Tasker S, Gunn-Moore DA, et al. Prognostic factors in cats with chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2007;21(5):906-916.
26. Jacob F, Polzin DJ, Osborne CA, et al. Evaluation of the association between initial proteinuria and morbidity rate or death in dogs with naturally occurring chronic renal failure. JAVMA. 2005;226(3):393-400.
27. Syme HM, Markwell PJ, Pfeiffer D, Elliott J. Survival of cats with naturally occurring chronic renal failure is related to severity of proteinuria. J Vet Intern Med. 2006;20(3):528–535.
28. Grodecki KM, Gains MJ, Baumal R, et al. Treatment of X-linked hereditary nephritis in Samoyed dogs with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. J Comp Pathol. 1997;117(3):209–225.
29. Grauer GF, Greco DS, Getzy DM, et al. Effects of enalapril versus placebo as a treatment for canine idiopathic glomerulonephritis. J Vet Intern Med. 2000;14(5):526–533.
30. Mizutani H, Koyama H, Watanabe T, et al. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of benazepril in the treatment of chronic renal insufficiency in cats. J Vet Intern Med. 2006;20(5):1074-1079.
31. Schneider SM, Cianciolo RE, Nabity MB, et al. Prevalence of immune- complex glomerulonephritides in dogs biopsied for suspected glomerular disease: 501 cases (2007-2012). J Vet Intern Med. 2013;27 (suppl 1):S67-S75.
32. Cianciolo R, Hokamp J, Nabity M. Advances in the evaluation of canine renal disease. Vet J. 2016;215:21-29.
33. Hokamp JA, Cianciolo RE, Boggess M, et al. Correlation of urine and serum biomarkers with renal damage and survival in dogs with naturally occurring proteinuric chronic kidney disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2016;30(2):591-601.
34. Giori L, Tricomi FM, Zatelli A, et al. High-resolution gel electrophoresis and sodium dodecyl sulphate-agarose gel electrophoresis on urine samples for qualitative analysis of proteinuria in dogs. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2011;23(4):682-690.
35. Zhou X, Ma B, Lin Z, et al. Evaluation of the usefulness of novel biomarkers for drug-induced acute kidney injury in beagle dogs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;280(1):30-35.
36. Ilchyshyn NP, Villiers E, Monti P. Validation of a spectrophotometric method for GGT measurement in canine urine and determination of the urine GGT-to-creatinine ratio reference interval and biological variation in 41 healthy dogs. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2019;31(1):33-39.
37. Brunker JD, Ponzio NM, Payton ME. Indices of urine N-acetyl-beta- D-glucosaminidase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activities in clinically normal adult dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2009;70(2):297-301.

原文地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/569477317 |
|
 /3
/3 