金桔
金币
威望
贡献
回帖0
精华
在线时间 小时
|
登陆有奖并可浏览互动!
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册


×
Secretory Protein是指在细胞内合成后,分泌到细胞外起作用的蛋白质。分泌蛋白的N 端有一般由15~30 个氨基酸组成的信号肽。信号肽是引导新合成的蛋白质向分泌通路转移的短(长度5-30个氨基酸)肽链。常指新合成多肽链中用于指导蛋白质的跨膜转移(定位)的N-末端的氨基酸序列(有时不一定在N端)。使用SignalP 注释蛋白序列是否含有信号肽结构,使用TMHMM注释蛋白序列是否含有跨膜结构,最终筛选出含有信号肽结构并且不含跨膜结构的蛋白为分泌蛋白。
软件Software
- SignalP V6.0
- SignalP 6.0 预测来自古细菌、革兰氏阳性细菌、革兰氏阴性细菌和真核生物的蛋白质中存在的信号肽predicts signal peptides and the location of their cleavage sites in proteins from Archaea, Gram-positive Bacteria,及其切割位点的位置。Gram-negative Bacteria and Eukarya.在细菌和古细菌中,SignalP 6.0 可以区分五种类型的信号肽:In Bacteria and Archaea, SignalP 6.0 can discriminate between five types of signal peptides:
- Sec/SPI:由 Sec 转座转运,并由信号肽酶 I (Lep) 切割的“标准”分泌信号肽;"Standard" secretory signal peptides transported by Sec translocon and cleaved by Signal Peptidase I (Lep).
- Sec/SPII:由 Sec 转座子运输,并由信号肽酶 II (Lsp) 切割的脂蛋白信号肽;lipoprotein signal peptides transported by the Sec translocon and cleaved by Signal Peptidase II (Lsp).
- Tat/SPI:由 Tat 转座子转运,并由信号肽酶 I (Lep) 切割的 Tat 信号肽;Tat signal peptides transported by the Tat translocon and cleaved by Signal Peptidase I (Lep).
- Tat/SPII:由 Tat 转位子转运,并由信号肽酶 II (Lsp) 切割的 Tat 脂蛋白信号肽;Tat lipoprotein signal peptides transported by Tat translocon & cleaved by Signal Peptidase II (Lsp).
- Sec/SPIII:由 Sec 转位子运输,并由信号肽酶 III (PilD/PibD) 切割的菌毛蛋白和菌毛蛋白样信号肽。Pilin & pilin-like signal peptides transported by Sec translocon & cleaved by Signal Peptidase III (PilD/PibD).
- 此外,SignalP 6.0 预测信号肽的区域。Additionally, SignalP 6.0 predicts the regions of signal peptides.根据类型,预测 n、h 和 c 区域以及其他显着特征的位置。Depending on the type, the positions of n-, h- and c-regions as well as of other distinctive features are predicted.
SignalP和TMHMM对于学术用户免费,但是需要填写相关信息和邮箱,以接收下载链接(4h有效时间)。
软件安装Installation of Softwares
安装SignalP 6.0
- 下载
访问SignalP V6.0网站,找到“Download”,填写相关信息,获取下载链接,下载得到“signalp-6.0.fast.tar.gz”。有两个模式可以选择——“slow_sequential”和“fast"。前者runs the full model sequentially, taking the same amount of RAM as fast but being 6 times slower;后者uses a smaller model that approximates the performance of the full model, requiring a fraction of the resources and being significantly faste。本教程下载的是fast模式。
- 安装Installation
- 安装依赖Dependencies
- Python
- matplotlib>3.3.2
- numpy>1.19.2
- torch>1.7.0
pip install torch
- tqdm>4.46.1
- 安装SignalP 6.0
# 解压缩安装文件 tar zxvf signalp-6.0.fast.tar.gz # 进入解压后的软件目录,在终端运行 python setup.py install # 测试安装 signalp6 --help
安装TMHMM V2.0c
软件用法Usage
SignalP 6.0
预测Prediction
A command takes the following form
signalp6 --fastafile /path/to/input.fasta --organism other --output_dir path/to/be/saved --format txt --mode fast
- fastafile 输入文件为FASTA格式的蛋白序列文件Specifies the fasta file with the sequences to be predicted.。
- organism is either other or Eukarya. Specifying Eukarya triggers post-processing of the SP predictions to prevent spurious results (only predicts type Sec/SPI).
- format can take the values txt, png, eps, all. It defines what output files are created for individual sequences. txtproduces a tabular .gff file with the per-position predictions for each sequence. png, eps, all additionally produce probability plots in the requested format. For larger prediction jobs, plotting will slow down the processing speed significantly.
- mode is either fast, slow or slow-sequential. Default is fast, which uses a smaller model that approximates the performance of the full model, requiring a fraction of the resources and being significantly faster. slow runs the full model in parallel, which requires more than 14GB of RAM to be available. slow-sequential runs the full model sequentially, taking the same amount of RAM as fast but being 6 times slower. If the specified model is not installed, SignalP will abort with an error.
输出Outputs
- output_dir/output.gff3:仅包含含有信号肽的序列信息;
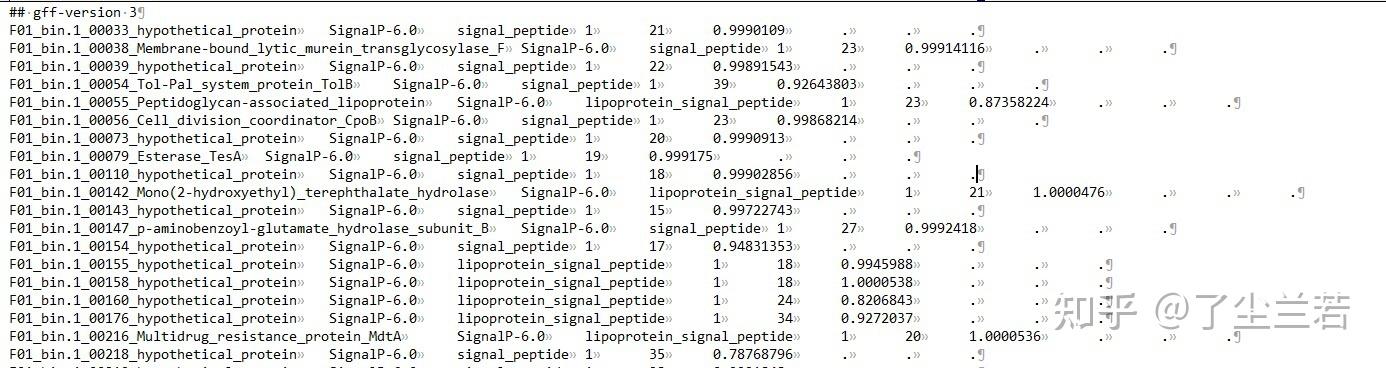
- output_dir/prediction_results.txt:包含了输入文件中的所有序列(不重要);
- output_dir/region_output.gff3:包含所有的信号肽区域信息。
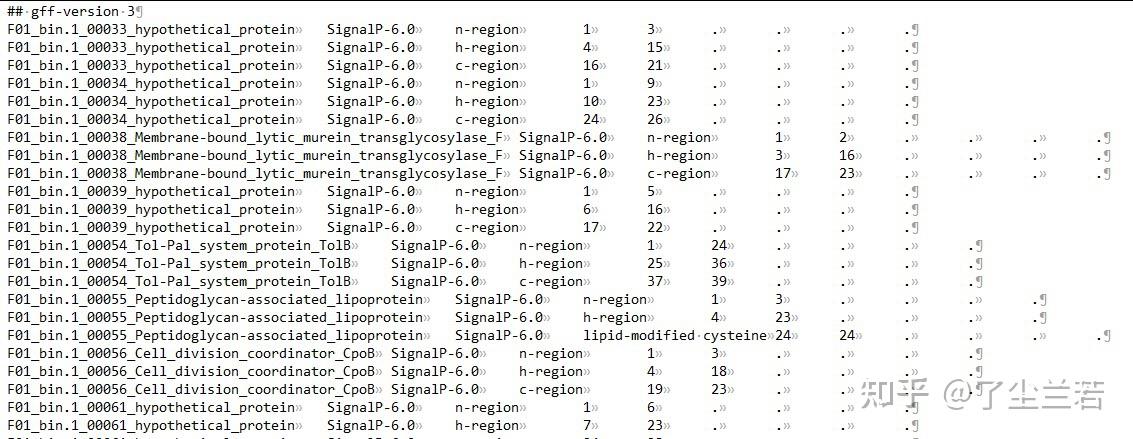
- n-region: The n-terminal region of the signal peptide. Reported for Sec/SPI, Sec/SPII, Tat/SPI and Tat/SPII. Labeled as N
- h-region: The center hydrophobic region of the signal peptide. Reported for Sec/SPI, Sec/SPII, Tat/SPI and Tat/SPII. Labeled as H
- c-region: The c-terminal region of the signal peptide, reported for Sec/SPI and Tat/SPI.
- Cysteine: The conserved cysteine in +1 of the cleavage site of Lipoproteins that is used for Lipidation. Labeled as c.
- Twin-arginine motif: The twin-arginine motif at the end of the n-region that is characteristic for Tat signal peptides. Labeled as R.
- Sec/SPIII: These signal peptides have no known region structure.
批处理与结果优化
脚本名:run_SignalP.pl
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
use warnings;
# Author: Liu Hualin
# Date: Oct 14, 2021
open IDNOSEQ, ">IDNOSEQ.txt" || die;
my @faa = glob("*.faa");
foreach (@faa) {
$_ =~ /(.+).faa/;
my $str = $1;
my $out = $1 . ".nodesc";
my $sigseq = $1 . ".sigseq";
my $outdir = $1 . "_signalp";
open IN, $_ || die;
open OUT, ">$out" || die;
while (<IN>) {
chomp;
if (/^(>\S+)/) {
print OUT $1 . "\n";
}else {
print OUT $_ . "\n";
}
}
close IN;
close OUT;
my %hash = idseq($out);
system("signalp6 --fastafile $out --organism other --output_dir $outdir --format txt --mode fast");
my $gff = $outdir . "/output.gff3";
if (! -z $gff) {
open IN, "$gff" || die;
<IN>;
open OUT, ">$sigseq" || die;
while (<IN>) {
chomp;
my @lines = split /\t/;
if (exists $hash{$lines[0]}) {
print OUT ">$lines[0]\n$hash{$lines[0]}\n";
}else {
print IDNOSEQ $str . "\t" . "$lines[0]\n";
}
}
close IN;
close OUT;
}
system("rm $out");
system("mv $sigseq $outdir");
}
close IDNOSEQ;
sub idseq {
my ($fasta) = @_;
my %hash;
local $/ = ">";
open IN, $fasta || die;
<IN>;
while (<IN>) {
chomp;
my ($header, $seq) = split (/\n/, $_, 2);
$header =~ /(\S+)/;
my $id = $1;
$hash{$id} = $seq;
}
close IN;
return (%hash);
}
将run_SignalP.pl与后缀名为“.faa”的FASTA格式文件放在同一目录下,在终端中运行如下代码:
perl run_SignalP.pl
结果解读Output interpretation
*代表输入文件的名字。
- *_signalp/output.gff3:仅包含含有信号肽的序列信息;
- *_signalp/prediction_results.txt:包含了输入文件中的所有序列(不重要);
- *_signalp/region_output.gff3:包含所有的信号肽区域信息;
- *_signalp/*.sigseq:存储所有信号肽的氨基酸序列文件,可用作TMHMM的输入文件。
TMHMM
预测
离线版总是报错,找不出原因,因此使用网页服务器进行,输入文件为上述生成的“*_signalp/*.sigseq”,将其上传至网页版TMHMM,提交任务,等待结果即可。
结果展示
TMHMM可以输出多种格式的结果文件,具体请参考其官方说明。
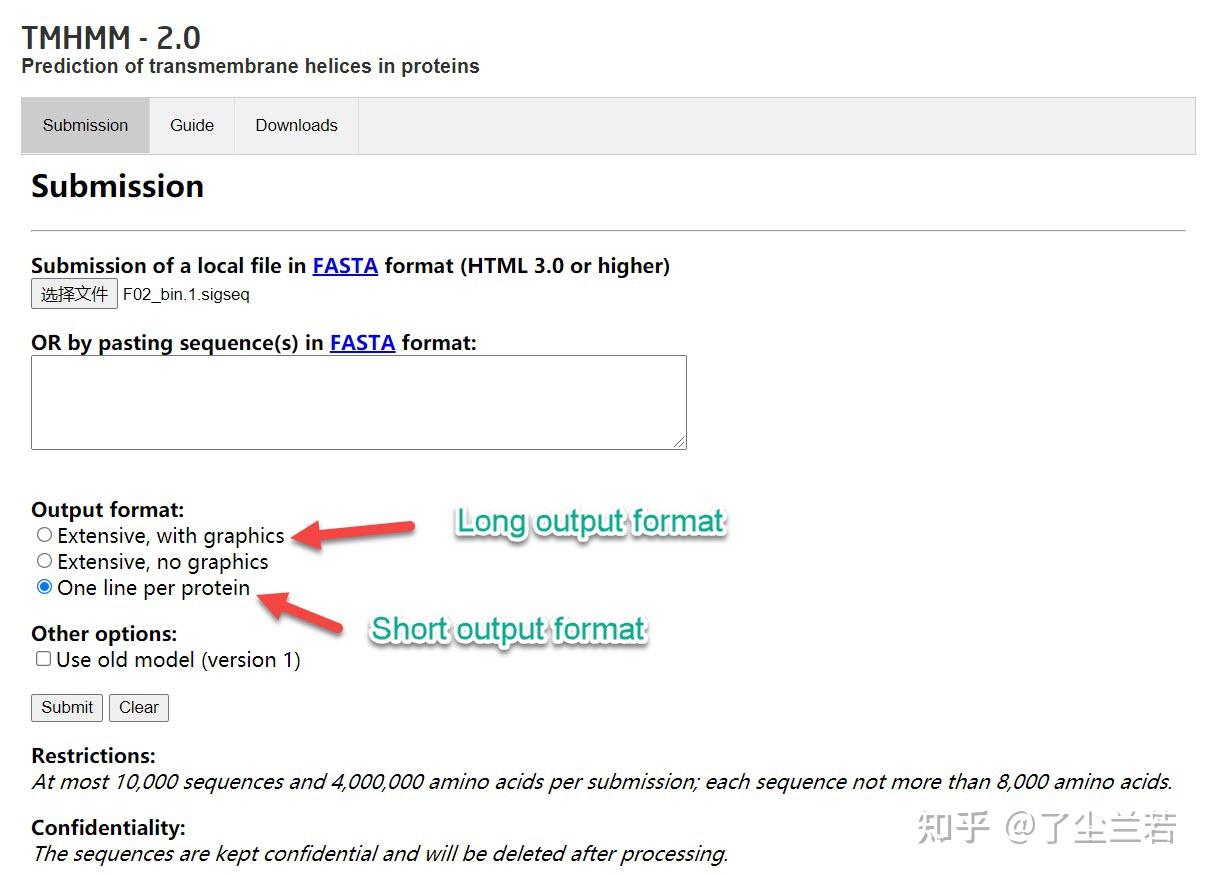
在TMHMM网站提交任务
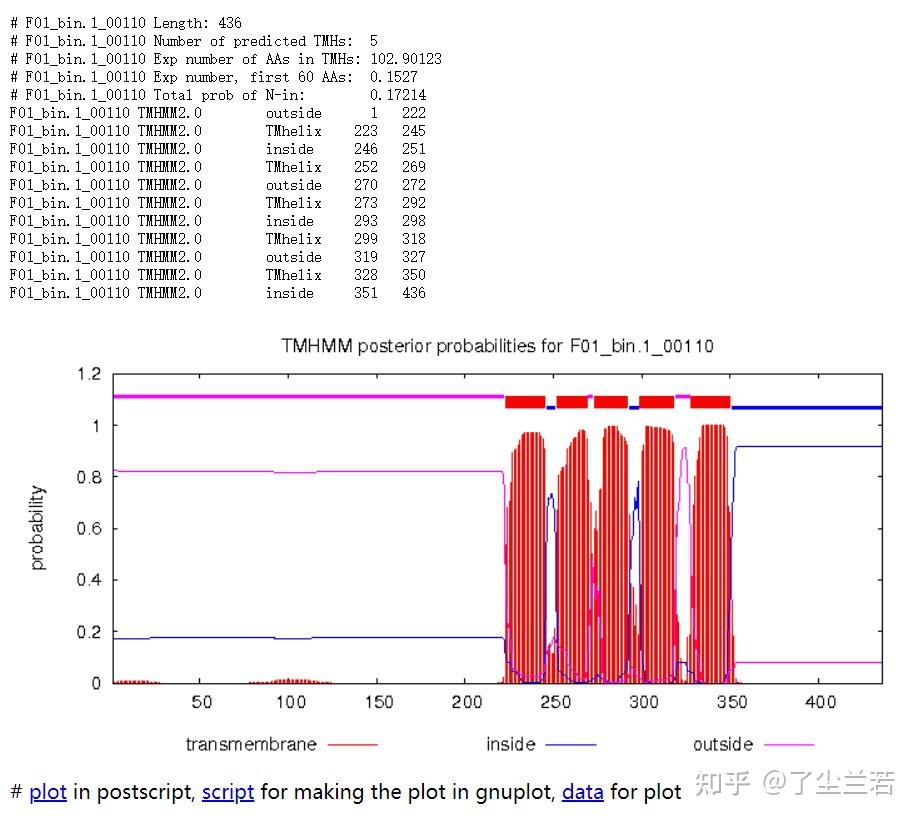
- Long output format
- Length: 蛋白序列的长度。The length of the protein sequence.
- Number of predicted TMHs:预测到的跨膜螺旋的数量。The number of predicted transmembrane helices.
- Exp number of AAs in TMHs:跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。The expected number of amino acids intransmembrane helices. 如果此数字大于 18,则很可能是跨膜蛋白(或具有信号肽)。If this number is larger than 18 it is very likely to be a transmembrane protein (OR have a signal peptide).
- Exp number, first 60 AAs:在蛋白的前60个氨基酸中跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。The expected number of amino acids in transmembrane helices in the first 60 amino acids of the protein.如果该数字超过几个,你应该被警告在 N 端预测的跨膜螺旋可能是一个信号肽。If it more than a few, you are warned that a predicted transmembrane helix in the N-term could be a signal peptide.
- Total prob of N-in:N端在膜的细胞质一侧的总概率。The total probability that the N-term is on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane.
- POSSIBLE N-term signal sequence:当“Exp number, first 60 AAs”大于 10 时产生的警告。A warning that is produced when "Exp number, first 60 AAs" is larger than 10.
- 蛋白F01_bin.1_00110共计436个氨基酸,有5个跨膜螺旋结构。
- 蛋白F01_bin.1_00142共计557个氨基酸,所有序列均在膜外,即该序列编码的是分泌蛋白。
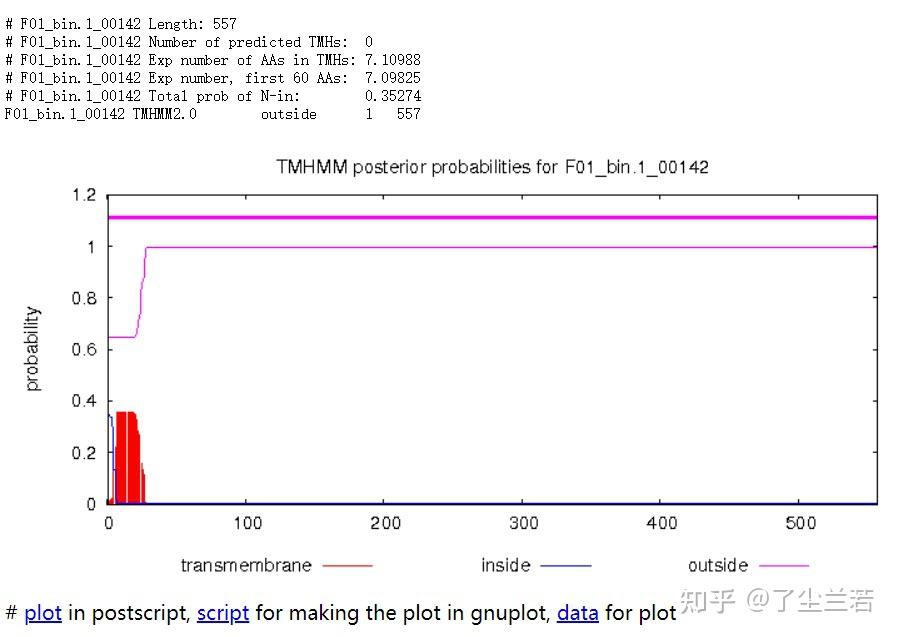
- Short output format
- "len=": 蛋白序列的长度。The length of the protein sequence.
- "ExpAA=":跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。The expected number of amino acids intransmembrane helices.如果此数字大于 18,则很可能是跨膜蛋白(或具有信号肽)。If this number is larger than 18 it is very likely to be a transmembrane protein (OR have a signal peptide).
- "First60=":在蛋白的前60个氨基酸中跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。The expected number of amino acids in transmembrane helices in the first 60 amino acids of the protein.如果该数字超过几个,你应该被警告在 N 端预测的跨膜螺旋可能是一个信号肽。If it more than a few, you are warned that a predicted transmembrane helix in the N-term could be a signal peptide.
- "PredHel=":预测到的跨膜螺旋的数量。The number of predicted transmembrane helices by N-best.
- "Topology=":N-best 预测的拓扑结构。The topology predicted by N-best.拓扑是由跨膜螺旋的位置给出的,如果螺旋在内部,则由“i”分隔,如果螺旋在外部,则由“o”分隔。'i7-29o44-66i87-109o'意味着它从膜内开始,在位置7到29有一个预测的TMH,30-43在膜外,然后是位置44-66的TMH。
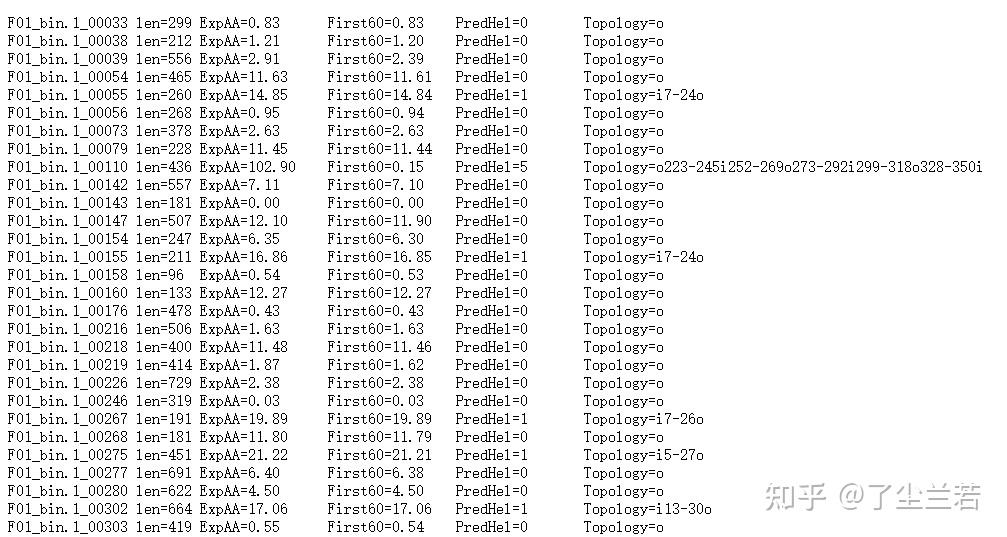
结果汇总
通过网页版预测我们仅得到了一个列表文件(Short output format),该文件需要自己复制网页内容粘贴到新文件中,我将其命名为*_TMHMM_SHORT.txt,并将其存放在*_signalp目录中,该目录是由run_SignalP.pl生成的。下面我将会统计各个基因组中信号肽蛋白的总数量、分泌蛋白数量和跨膜蛋白数量到文件Statistics.txt中,并分别提取每个基因组的分泌蛋白序列到*_signalp/*.secretory.faa文件中,提取跨膜蛋白序列到*_signalp/*.membrane.faa文件中。该过程将通过tmhmm_parser.pl完成。
#!/usr/bin/perl use strict; use warnings; # Author: Liu Hualin # Date: Oct 15, 2021 open OUT, ">Statistics.txt" || die; print OUT "Strain name\tSignal peptide numbers\tSecretory protein numbers\tMembrane protein numbers\n"; my @sig = glob("*_signalp"); foreach my $sig (@sig) { $sig=~/(.+)_signalp/; my $str = $1; my $tmhmm = $sig . "/$str" . "_TMHMM_SHORT.txt"; my $fasta = $sig . "/$str" . ".sigseq"; my $secretory = $str . ".secretory.faa"; my $membrane = $str . ".membrane.faa"; open SEC, ">$secretory" || die; open MEM, ">$membrane" || die; my $out = 0; my $on = 0; my %hash = idseq($fasta); open IN, $tmhmm || die; while (<IN>) { chomp; $_=~s/[\r\n]+//g; # print $_ . "\n"; my @lines = split /\t/; if ($lines[5] eq "Topology=o") { $out++; print SEC ">$lines[0]\n$hash{$lines[0]}\n"; }else { $on++; print MEM ">$lines[0]\n$hash{$lines[0]}\n"; } } close IN; close SEC; close MEM; system("mv $secretory $membrane $sig"); my $total = $out + $on; print OUT "$str\t$total\t$out\t$on\n"; } close OUT; sub idseq { my ($fasta) = @_; my %hash; local $/ = ">"; open IN, $fasta || die; <IN>; while (<IN>) { chomp; my ($header, $seq) = split (/\n/, $_, 2); $header =~ /(\S+)/; my $id = $1; $hash{$id} = $seq; } close IN; return (%hash); }
运行方法:将tmhmm_parser.pl放在*_signalp的上一级目录下,*_signalp目录中必须包含*_TMHMM_SHORT.txt文件和*.sigseq文件。在终端运行如下代码:
perl tmhmm_parser.pl
脚本获取
本文脚本见GitHub。
敬告:使用文中脚本请引用本文网址,请尊重本人的劳动成果,谢谢!Notice: When you use the scripts in this article, please cite the link of this webpage. Thank you!
参考
原文链接:SignalP+TMHMM预测微生物分泌蛋白 | liaochenlanruo
转载请注明出处!
http://weixin.qq.com/r/HUzl-XvE6CaXrT_e9xkP (二维码自动识别)
原文地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/423757806 |
|
 /3
/3 